As global efforts to combat climate change intensify, maritime shipping companies must prioritize emissions reduction and compliance with corporate sustainability reporting frameworks.
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is shaping the future of emissions reporting for shipping companies. CSRD now requires accurate measures and disclosure of CO₂e emissions (Carbon Dioxide Equivalent).
With regulations tightening across EU countries, freight forwarders and vessel operators must integrate structured sustainability data into their management reports. That’s the only way to meet CSRD requirements and enhance their sustainability performance.
This guide explores the impact of CO₂e reporting, CSRD compliance, and actionable strategies to ensure regulatory alignment while reducing carbon emissions in maritime operations.
Understanding CO₂e and Its Role in Maritime Sustainability
What is CO₂e and Why Does It Matter in Maritime Shipping?
CO₂e (Carbon Dioxide Equivalent) is a metric that standardizes the impact of multiple greenhouse gases, including methane (CH₄) and nitrous oxide (N₂O). It expresses their global warming potential relative to carbon dioxide (CO₂).
By using CO₂e emissions as a benchmark, maritime companies can better assess their total climate impact. This allows them to track emissions more accurately and implement effective sustainability strategies.
The maritime industry contributes approximately 3% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Fuel combustion in shipping vessels is the primary source of indirect emissions.
Reducing emissions intensity is critical for ensuring compliance with European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) and meeting global climate targets set by international agreements.
The Growing Regulatory Pressure on the Shipping Industry
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has established a GHG reduction strategy. This strategy mandates shipping companies to implement emission reduction strategies. The goal is to achieve a 50% reduction in CO₂ emissions by 2050 compared to 2008 levels.
This aligns with the European Union’s sustainability objectives, which require businesses to reduce their carbon footprint and report on their environmental impact.
Additionally, the Paris Agreement has influenced maritime industry policies by setting legally binding emission reduction commitments. As a result, shipping companies must implement strategies that contribute to reducing emissions, improving operational efficiencies, and meeting CSRD reporting requirements.
CSRD and Its Impact on Maritime Shipping
What is the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)?
The CSRD replaces the Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD). CSRD significantly expands sustainability disclosure requirements for companies operating in EU-regulated markets.
Designed to enhance corporate sustainability reporting, the directive mandates standardized and transparent disclosures under the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS).
Shipping companies and freight forwarders in EU member countries must include emission reporting in their management reports. This ensures that stakeholders and investors have access to reliable emissions data.
Who Needs to Comply with CSRD in the Maritime Sector?
Companies must comply with CSRD requirements if they meet at least two of the following three criteria:
- 250 employees or more.
- €40 million net turnover or more.
- €20 million in total assets or more.
Additionally, non-EU companies generating €150 million or more in the EU market must comply with CSRD reporting requirements starting in 2028.
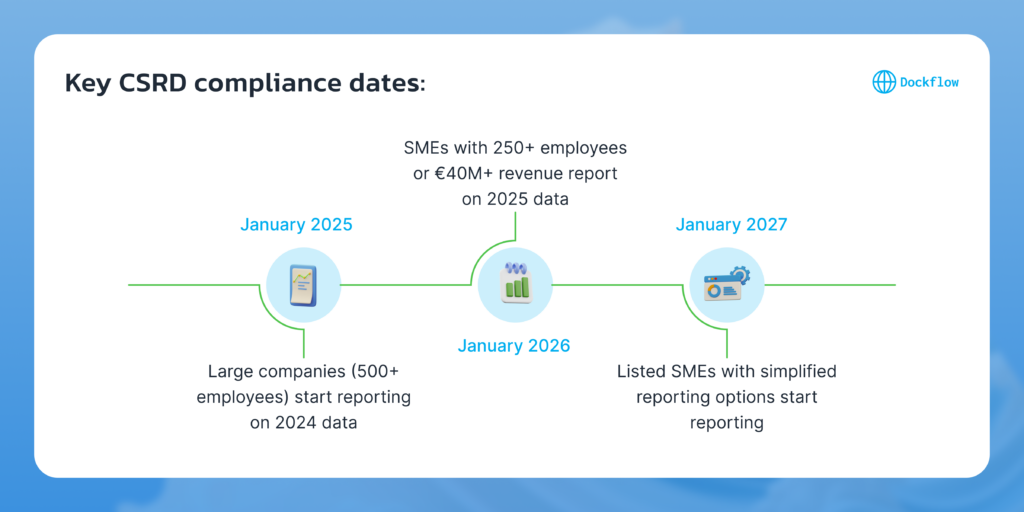
Key CSRD Deadlines for Maritime Shipping
- FY 2024: Large companies under NFRD begin CSRD-aligned reporting in 2025.
- FY 2025: Other large companies must submit CSRD reports in 2026.
- FY 2026: Listed SMEs in shipping must comply by 2027.
- FY 2028: Non-EU companies with €150 million turnover in the EU report by 2029.
Measuring and Reporting CO₂e in Compliance with CSRD
The Role of CO₂e in Environmental Reporting
Accurate CO₂e emissions tracking is essential for CSRD-compliant sustainability reporting. Companies must align their emissions calculations with European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) to ensure full transparency and accountability.
How to Accurately Measure CO₂e in Maritime Shipping
Fuel-based approach
This method calculates CO₂e emissions based on the type, quality, and quantity of fuel consumed by a vessel. Different fuels, such as heavy fuel oil (HFO), liquefied natural gas (LNG), ammonia, and biofuels, have varying emissions factors.
To ensure CSRD-compliant reporting, shipping companies must consider fuel mix, combustion efficiency, and supply chain emissions.
Distance-based calculations
Tracking emissions intensity per voyage or cargo unit allows companies to measure the environmental impact of each shipment. By incorporating factors like cargo weight, fuel efficiency, and travel distance, companies can improve operational efficiencies and reduce emissions.
Well-to-Wake (WTW) vs. Tank-to-Wake (TTW)
WTW calculations assess emissions from fuel production, refining, and distribution through final consumption. This method offers a comprehensive life cycle analysis.
TTW measurements focus solely on direct fuel combustion emissions, providing insights into a vessel’s operational carbon footprint.
Using a CO₂e CSRD Maritime Shipping Calculator
Dockflow’s RealCalc® CO₂e tracker automates real-time emissions monitoring and ensures CSRD-compliant reporting for freight forwarders and shipping companies. With AI-powered analytics, businesses can accurately track carbon emissions and streamline sustainability reporting processes.
Strategies for Maritime Shipping Companies to Reduce CO₂e and Ensure CSRD Compliance
Optimize Fuel Efficiency and Reduce Carbon Intensity
Improving fuel efficiency is crucial for reducing emissions. Companies must transition to low-carbon fuels, implement AI-powered route optimization, and enhance ship energy efficiency.
Shift to Sustainable Fuels and Alternative Energy Sources
Adopting biofuels, hydrogen, and ammonia can help lower emissions. Investing in shore-side electricity (cold ironing) enables vessels to reduce fuel consumption when docked.
Improve Freight Consolidation and Logistics Optimization
By minimizing empty container movements and improving cargo utilization, companies can lower emissions. Collaborative freight strategies can also enhance efficiency across the supply chain.
Leverage Digital Reporting and ESG Analytics Tools
AI-powered ESG analytics tools ensure CSRD-compliant reporting, allowing companies to automate data collection and emissions tracking.
Ensure Transparency with Suppliers and Stakeholders
Collaboration with supply chain partners helps improve Scope 3 emissions tracking, ensuring full sustainability disclosure and regulatory alignment.
Business Benefits of CSRD Compliance in Maritime Shipping
Strengthening Brand Reputation and Stakeholder Trust
Companies that meet CSRD requirements enhance their credibility with investors and regulators.
Avoiding Regulatory Fines and Market Restrictions
Non-compliance with CSRD reporting requirements can result in financial penalties and loss of market access.
Gaining a Competitive Advantage in Global Logistics
Sustainable companies attract eco-conscious clients and freight partners, leading to long-term business success.
Get Started with CSRD-Compliant CO₂e Reporting Today
Dockflow’s RealCalc® CO₂e emissions calculator automates CSRD-compliant emissions tracking, ensuring accurate sustainability reporting for maritime shipping companies.





